What Does a Neuron Look Like?
Unveiling the Intricacies of the Brain’s Building Blocks
The Question is What Does a Neuron Look Like? and here simple answer with details. The human brain is an astonishing organ, with billions of neurons intricately wired together, forming the basis of our cognitive functions and thoughts. Have you ever wondered what these fundamental building blocks of the brain, neurons, actually look like? In this article, we will take a closer look at the structure and appearance of neurons, delving into their fascinating world. Here Diagram of Neuron Look Like below
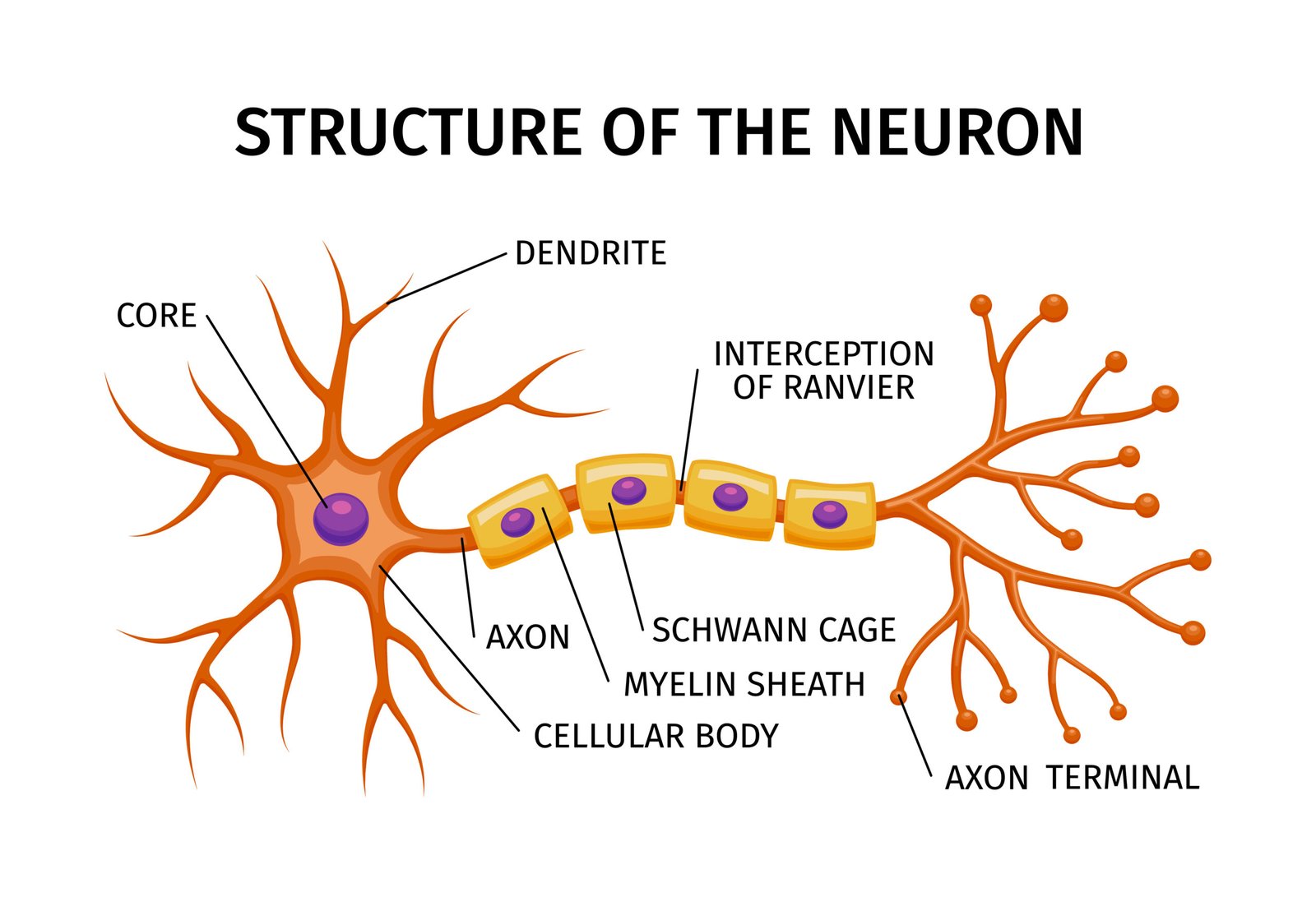
The Basics of Neurons
Neurons Look , often referred to as nerve cells, are the primary functional units of the nervous system. They are responsible for transmitting information throughout the body, enabling us to perceive and react to our environment. Neurons come in various shapes and sizes, each adapted for specific functions.
Neuron Anatomy
2.1. Dendrites: The Receiving End
Dendrites are tree-like branches extending from the neuron’s cell body. They receive signals from other neurons Look or sensory receptors, acting as the input zone for information.
2.2. Cell Body: The Core of Operations
The cell body, or soma, is the neuron’s control center. It processes incoming signals and generates an appropriate response. It also contains the nucleus, which houses the neuron’s genetic information.
2.3. Axon: The Information Highway
The axon is a lengthy and slender extension responsible for transmitting signals away from the cell body. It’s coated with a myelin sheath, which enhances signal transmission. Axons can be incredibly long, enabling communication across vast distances within the body.
Neurons in Action
1. Neuron Communication
Neurons communicate through electrical impulses and chemical signals. When a neuron receives a signal, it initiates an electrical impulse that travels down the axon. At the end of the axon, chemical neurotransmitters are released to transmit the signal to the next neuron.
2. Role in Information Processing
Neurons work together in complex networks to process information. They integrate signals from multiple sources and make decisions on how to respond. This intricate dance of neurons underlies our thoughts, emotions, and actions.
Diversity in Neuron Appearance
1. Variations in Neuron Shapes
Neurons come in a wide variety of shapes, ranging from simple and unipolar to highly complex and multipolar. This diversity allows them to perform specialized functions in different parts of the nervous system.
2. Neuron Colors and Staining
Staining techniques can reveal the presence of specific proteins and structures within neurons. This helps researchers identify and study different types of neurons in detail.
State-of-the-Art Imaging Techniques
1. Light Microscopy
Light microscopy provides a basic view of neurons but lacks the resolution needed to examine fine details. It’s useful for observing larger structures within neurons.
2. Electron Microscopy
Electron microscopy offers much higher resolution and can capture ultra-fine details of neuron structure. It’s an invaluable tool for neuroscientists.
Challenges in Visualizing Neurons
Despite advancements in imaging techniques, visualizing neurons in their entirety remains a challenge due to their immense complexity and density.
The Beauty of Neuron Art
Some scientists and artists have merged science and art to create stunning visual representations of neurons, showcasing their intricate beauty.
Neurons in Pop Culture
Neurons have made appearances in various forms of pop culture, from literature to movies, reflecting their significance in our understanding of the brain.
The Future of Neuron Imaging
Advancements in technology continue to push the boundaries of neuron imaging. Breakthroughs are on the horizon, promising even greater insights into the brain’s workings.
Unlocking the Secrets of the Brain
Studying neurons is key to unraveling the mysteries of the brain and finding treatments for neurological disorders.
Conclusion
In conclusion, neurons Look are the essential building blocks of the brain, responsible for processing information and enabling our cognitive functions. While visualizing neurons remains a challenge, state-of-the-art imaging techniques and artistic representations allow us to appreciate their beauty and complexity.
